|
Potential energy is defined as the energy stored in an object
because of its position. An example is the potential energy of an object above
the surface of the earth in the earth's gravitational field. Potential energy
also applies to energy due to separation of electrical charge and to energy
stored in a spring, in other words, energy due to position of any force field.
As an example, consider the energy stored in
hydrogen and oxygen as potential energy to be released on burning. Burning
changes their relative separation distance from the elemental form to the
compound form as water releases the potential energy.
When discussing mechanical potential energy, we look
at the position of an object. The measure of an object's position is its
vertical distance above a reference point. The reference point is normally the
earth's surface, but can it be any point. The potential energy of the object
represents the work required to elevate the object to that position from the
reference point. Potential energy is mathematically represented by Equation
5-1.
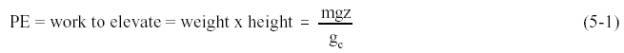
where:

It should be noted the g,, is used only when using
the English system of measurement.
Example: What
is the potential energy of a 501bm object suspended 10 feet above the ground?
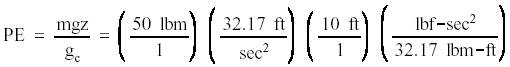
Answer: PE
= 500 ft-lbf
|

