|
Alpha
decay is the emission of alpha particles (helium nuclei) which
may be represented as either 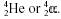 . He or When an unstable nucleus ejects an alpha
particle, the atomic number is reduced by 2 and the mass number decreased by 4.
An example is uranium-234 which decays by the ejection of an alpha particle
accompanied by the emission of a 0.068 MeV gamma. . He or When an unstable nucleus ejects an alpha
particle, the atomic number is reduced by 2 and the mass number decreased by 4.
An example is uranium-234 which decays by the ejection of an alpha particle
accompanied by the emission of a 0.068 MeV gamma.
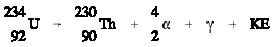
The combined kinetic energy of the daughter nucleus
(Thorium-230) and the a particle is designated as KE. The sum of the KE and the
gamma energy is equal to the difference in mass between the original nucleus
(Uranium-234) and the final particles (equivalent to the binding energy
released, since  m
= m
= 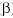 E). The alpha particle will carry off as much as
98% of the kinetic energy and, in most cases, can be considered to carry off
all the kinetic energy. E). The alpha particle will carry off as much as
98% of the kinetic energy and, in most cases, can be considered to carry off
all the kinetic energy.
Beta Decav (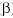 ) )
Beta
decay is the emission of electrons of nuclear rather than
orbital origin. These particles are electrons that have been expelled by
excited nuclei and may have a charge of either sign.
If both energy and momentum are to be conserved, a third
type of particle, the neutrino, v, must be involved. The neutrino is associated
with positive electron emission, and its antiparticle, the antineutrino, 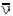 , is emitted with a negative
electron. These uncharged particles have only the weakest interaction with
matter, no mass, and travel at the speed of light. For all practical purposes,
they pass through all materials with so few interactions that the energy they
possess cannot be recovered. The neutrinos and antineutrinos are included here
only because they carry a portion of the kinetic energy that would otherwise
belong to the beta particle, and therefore, must be considered for energy and
momentum to be conserved. They are normally ignored since they are not
significant in the context of nuclear reactor applications. , is emitted with a negative
electron. These uncharged particles have only the weakest interaction with
matter, no mass, and travel at the speed of light. For all practical purposes,
they pass through all materials with so few interactions that the energy they
possess cannot be recovered. The neutrinos and antineutrinos are included here
only because they carry a portion of the kinetic energy that would otherwise
belong to the beta particle, and therefore, must be considered for energy and
momentum to be conserved. They are normally ignored since they are not
significant in the context of nuclear reactor applications.
Negative electron emission, represented as 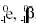 or simply as or simply as 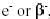 effectively converts a neutron
to a proton, thus increasing the atomic number by one and leaving the mass
number unchanged. This is a common mode of decay for nuclei with an excess of
neutrons, such as fission fragments below and to the right of the
neutron-proton stability curve (refer to Figure 6). An example of a typical
beta minus-decay reaction is shown below. effectively converts a neutron
to a proton, thus increasing the atomic number by one and leaving the mass
number unchanged. This is a common mode of decay for nuclei with an excess of
neutrons, such as fission fragments below and to the right of the
neutron-proton stability curve (refer to Figure 6). An example of a typical
beta minus-decay reaction is shown below.
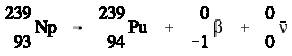
Positively charged electrons (beta-plus) are known as
positrons. Except for sign, they are nearly identical to their negatively
charged cousins. When a positron, represented as 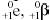 , or
simply as , or
simply as 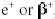 ,
is ejected from the nucleus, the atomic number is decreased by one and the mass
number remains unchanged. A proton has been converted to a neutron. An example
of a typical positron (beta-plus) decay is shown below. ,
is ejected from the nucleus, the atomic number is decreased by one and the mass
number remains unchanged. A proton has been converted to a neutron. An example
of a typical positron (beta-plus) decay is shown below.
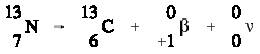
|

|






