|
Sexagesimal or North American System In the sexagesimal or North American system, the
circle is divided into 360 equal parts known as
DEGREES of arc, each degree into 60 equal parts
known as MINUTES of arc, and each minute
into 60 equal parts known as SECONDS of
arc. As an example, angles in this system are
written as 26304716.48 which is read as "two
hundred sixty-three degrees, forty-seven minutes,
and sixteen point four eight seconds of arc.
" In the United States, this is the most commonly
used system of angular measurement.
Centisimal or Metric System
In the centisimal or metric system, the full circle
is divided into four quadrants, and each quadrant
is divided into 100 equal parts known as
GRADS or GRADES. Each grad is further divided
into decimal parts. As an example, angles in
this system are written as 376g
.7289, or 376g
7289" which is read as
"three hundred seventy-six
point seven two eight nine grads," or as
"three hundred seventy-six grads, seventy-two centisimal
minutes, and eighty-nine centisimal seconds.
"
Mil System
In the mil system, the circle is divided into 6,400
equal parts known as MILS. The mil is divided
into decimal parts. As an example, angles in
this system are written as 1728.49 roils, which is
read as "one thousand seven hundred twenty-eight point
four nine mils." This system is used principally
by the artillery people. The significance of
this unit of angular measure is the fact that 1 mil
is the angle that will subtend 1 yd at a range of
1,000 yd.
The relationship among values in the three systems
of angular measure are as follows:

MORE UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
Aside from the units of measurement discussed
above, the EA must also deal with other
units of measurement, such as TIME, TEMPERATURE,
PRESSURE, and so forth. He must use
exact time in computing problems in
astronomy and some laboratory works. He must
be able to apply temperature corrections to his
tape readings. He must also evaluate the effect
of atmospheric pressure at different elevations
and get involved in some other types
of measure that will be discussed in the following
paragraphs.
Time Measurement
For practical purposes in everyday affairs and in
surveying, the measurement of time intervals is
of great concern. The time used in everyday life is
known as STANDARD TIME and is based on the
mean apparent revolution of the sun around the
earth because of the earths rotation on its axis.
Standard time is used in surveying to regulate the
normal days operations. But, when it is necessary
to observe the sun or the stars to determine
the azimuth of a line or the position of
a point on the earths surface, the surveyor uses three
other kinds of time. They are APPARENT (true)
SOLAR TIME, CIVIL (mean solar) TIME, and
SIDEREAL (star) TIME. You will learn more about
these different times when you study the chapter
on "Geodesy and Field Astronomy" in Engineering
Aid 1 & C.
In all four kinds of time, the basic
units of measure are the YEAR, DAY,
HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND of time.
The duration of any one of these
units is not the same for all kinds of time. For
example, the sidereal day is approximately 4 min
shorter than a standard- or civil-time day. In
the practice of surveying, it is customary to
say, or write, the time of day as the number of
hours, minutes, and seconds since midnight. Then
the recorded time would appear, for example,
as 16h37m52S.71 which is read as "sixteen
hours, thirty-seven minutes, and fifty-two point
seven one seconds of time."
Units of time measure are sometimes used to designate
the sizes of angles. The longitude of a point
on the earths surface is often expressed in this
manner. The relationship between the units of
time measure and the units of angular measure in
the sexagesimal system are as follows:
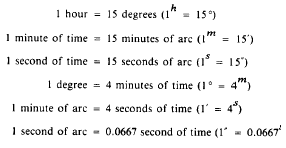
|
|

