|
MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISORS The maxillary central incisor (tooth #8 or #9) is illustrated in figures 4-27 and 4-28. Viewed mesially or distally, a maxillary central incisor looks like a wedge, with the point of the wedge at the incisal (cutting) edge of the tooth. Facial Surface-The facial surface resembles a thumbnail in outline. The mesial margin is nearly straight and meets the incisal edge at almost a 90 angle, but the distal margin meets the incisal edge in a curve. The incisal edge is straight, but the cervical margin is curved like a half moon. Two developmental grooves are on the facial surface.

Figure 4-23.\Vertical and horizontal overlap.

Figure 4-25.\Key to occlusion. Shows relationship of mandible to maxillae.

Figure 4-24.\Angle's classification.

Figure 4-26.\Normal cusp relations of posterior teeth.

Figure 4-27.\Surfaces of a maxillary central incisor. Lingual Surface\The lingual surface (fig. 4-28) is quite similar to the facial surface in outline except that it is slightly smaller in all dimensions. At the mesial and distal margins there are marginal ridges. Occasionally there is a cingulum at the junction of the lingual surface with the cervical line. Sometimes a deep pit, the lingual pit, is found in conjunction with a cingulum. Root Surface\As with all anterior teeth, the root of the maxillary central incisor is single. This root is from one and one-fourth to one and one-half times the length of the crown. Usually, the apex of the root is inclined slightly distally. MAXILLARY LATERAL INCISORS The maxillary lateral incisor (tooth #7 or #IO),
illustrated in figure 4-29, is much like the maxillary central incisor, except in size: it is shorter, narrower, and thinner.
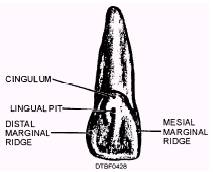
Figure 4-28.\Features of a lingual surface of maxillary central incisor.

Figure 4-29.\Surfaces of a maxillary lateral incisor. Facial Surface\The developmental grooves on the facial surface are not so evident as those of the central incisor. Of more significance, however, is the distoincisal angle, which is well-rounded with this curvature continuing to the cervical line. The mesiofacial angle is nearly straight to the cervical line. Lingual Surface\The shape of the lingual surface varies with the individual. In some persons it is markedly concave, almost spoon-like in appearance, and in others, it is flat. The lingual surface is almost the same as the facial surface. Root Surface\The root is conical (cone-shaped) but somewhat flattened mesiodistally.
|

