|
Nylon Flat Spotting If the aircraft stands in one place under a heavy static
load for several days, local stretching may cause an
out-of-round condition with a resultant thumping during
takeoff and landing.
Dual Installations
On dual-wheel installations, tires should be matched
according to the dimensions indicated in table
11-1. Tires vary somewhat in size between manufacturers
and can vary a great deal after being used.
When two tires are not matched, the larger one supports
most or all of the load. Since one tire is not designed
to carry this increase in load, a failure may result.
AIRCRAFT TUBES
Learning Objective: Identify
the procedures for the
selection, storage, and inspection of aircraft
tire tubes.
The purpose of the inner tube is to hold the air in the
tire. Tubes are identified by the type and size of the
tire in which they are to be used.
IDENTIFICATION
Tubes are designated for the tires in which they are
to be used. For example, a type I tube is designed for
use in a type I tire. The size of the tube is the size of
the tire in which it is designed to fit. Inner
tubes required to operate at 100 psi or higher
inflation pressures are usually reinforced with a
ply of nylon cord fabric around the inside circumference.
The reinforcement extends a minimum
of one-half inch beyond that portion of the tube
that contacts the rim.
Table 11-1.Tolerances for Diameters of Paired Tires in Dual
Installations
| Tire outside
diameter |
Maximum difference
in outside diameters |
| Less then
18 inches |
1/8 inch |
| 18 to 24
inches |
1/4 inch |
| 25 to 32
inches |
5/16 inch |
| 33 to 40
inches |
3/8 inch |
| 41 to 48
inches |
7/16 inch |
| 49 to 55
inches |
1/2 inch |
| 56 to 65
inches |
9/16 inch |
| More than
65 inches |
5/8 inch |
Type III and type VII inner tubes have radial vent ridges
molded on the surface, as shown in figure 11-29.
These vent ridges relieve air trapped between the
casings and the inner tube during inflation. Inner
tube valves are designed to fit specific wheel
rims. However, special valve-bending configurations
or extensions to provide access to the valve
stem when you are servicing the tire may be required.
TUBE STORAGE
Tubes should be stored under the same conditions as
new tires. New tubes should be stored in their original
containers. Used tubes should be partially inflated
(to avoid creasing), dusted with talc (to prevent
sticking), and stored in the same manner as tires.
Each tube should be plainly marked to identify contents,
size, type, cure date, and stock number. Under
no circumstances should inner tubes be hung over
nails or hooks.
INSPECTION
Inner tubes should be inspected and classified as serviceable
or nonserviceable. Usually, leaks due to punctures,
breaks in the tire, and cuts can be detected by
the eye. Small leaks may require a soapy water check.
Complete submersion in water is the best way to
locate small leaks. If the tube is too large to be submerged,
spread soapy water over the entire surface and
examine carefully for air bubbles. The valve stem
and valve base should be swished around to break
any temporary seals. The tube should be checked
for bent or broken valve stems and stems with
damaged threads.
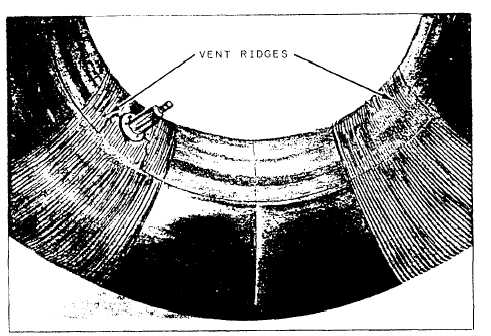
Figure
11-29.Inner tube vent ridges.
|


|

