|
REGULAR PYRAMIDS AND RIGHT
CIRCULAR CONES
A PYRAMID is a solid figure, the lateral faces
of which are triangles. (See fig. 18-16.) A
REGULAR PYRAMID has all of its lateral faces
equal.
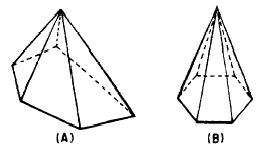
Figure 18-16.-(A) Irregular pyramid; (B)
regular pyramid.
A regular pyramid with a very large number of
lateral faces would have a base polygon with many
sides. If the number of sides is sufficiently large, the base polygon is
indistinguishable from a circle and the surface formed by the
many lateral faces becomes a smoothly curved
surface. The solid figure thus formed is
a RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE. (See fig. 18-17.)
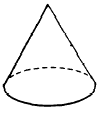
Figure 18-17. -Right circular cone.
Slant Height
The slant height of a regular pyramid is the perpendicular
distance from the vertex to the center
of any side of the base. For example, the
length of line AV in figure 18-18 (A) is the slant
height. The slant height of a right circu base. Such a line is
perpendicular to a line tangent to the base
at the point where the slant height
intersects the base. (See fig. 18-18 (B).) Lines
AV, BV, and CV in figure 18-18 (B) are all
slant heights.
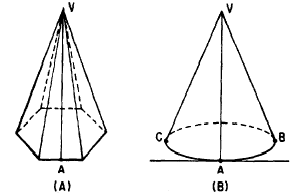
Figure 18-18.-(A) Slant height of a regular pyramid;
(B) slant height of a right circular cone.
Lateral Area
The lateral area of a pyramid is the sum of
the areas of its lateral faces. If the pyramid is
regular, its lateral faces have equal bases; furthermore,
the slant height is the altitude of each
face. Therefore, the area of each lateral face
is one-half the slant height multiplied by the
length of one side of the base polygon. Since the
sum of these sides is the perimeter of the base,
the total lateral area of the pyramid is the
product of one-half its slant height multiplied by the perimeter of its base.
Using s to represent slant height and P to
represent the perimeter of the base,
the formula is as follows:
Lateral Area = 1/2 aP
A right circular cone can be considered as a regular
pyramid with an infinite number of faces. Therefore,
using C to represent the circumference of the base, the formula for the lateral
area of a right circular cone is
Lateral Area = 1/2 sC
Volume
The volume of a pyramid is determined by
its
base and its altitude, as is the case with other
solid figures. Experiments show that the volume
of any pyramid is-one-third of the prod stated
as a formula with V representing volume, B representing the area of the base,
and h representing height (altitude),
as follows:
V = 1/3 Bh
The formula for the volume of a pyramid does
not depend in any way upon the
number of faces. Therefore, we use the
same formula for the volume of a right
circular cone. Since the base is
a circle, we replace B with pr2 (where
r is the radius of the base). The formula for
the volume of a right circular cone is then

Practice problems:
1. Find the lateral area of a regular pyramid with
a 5-sided base measuring 3 inches on each side,
if the slant height is 12 inches.
2. Find the lateral area of a right circular cone
whose base has a diameter of 6 cm and whose slant
height is 14 cm.
3. Find the volume of a regular pyramid with a square
base measuring 4 cm on each side, if the
vertex is 9 cm above the base.
4. Find the volume of a right circular cone
whose base has a diameter of 14 inches, if the
altitude is 21 inches.
Answers:
1. 90 in. sq
2. 132 cm sq
3. 48 cu cm
4. 1077 cu in.
|

